Radiographic diagnostics
Even the most thorough and experienced dental practitioner is not able to make a fully accurate diagnosis (and thus carry out the correct treatment) without appropriate diagnostic equipment. You have no need to worry about diagnostic tools and devices at Vinci Clinic, because we were the first dental clinic in Lodz to use panoramic X-ray (1991), semi-direct digital radiography (1999), digital radiography (2003), and cone beam computed tomography CBCT (2009).
Modern diagnostics cannot do without the support of dental radiology. Depending on the clinical situation, different types of examinations are performed – ranging from single tooth images to 3D tomography.
X-RAY
Radiographs
A dental radiograph covers one to three teeth together with adjacent tissues. It allows lesions within the dental tissues and the surrounding bone that are not visible during the clinical examination to be observed and analyzed. It can also be used in the evaluation of tooth pain, in the detection of carious lesions in various locations and in endodontic treatment (evaluation of the condition of root canals).
Orthopantomogram
A pantomogram provides information about the patient’s entire dentition, the tissues surrounding the teeth, and the maxilla and mandible. A pantomogram is an overview examination, which allows the dentist to detect all abnormalities and inflammatory lesions that are not visible to the naked eye.
Cephalometric radiograph
Cephalometric radiographs are most commonly used in connection with orthodontic treatment. The dentist takes measurements to diagnose malocclusion and assess the direction of the patient’s facial growth.
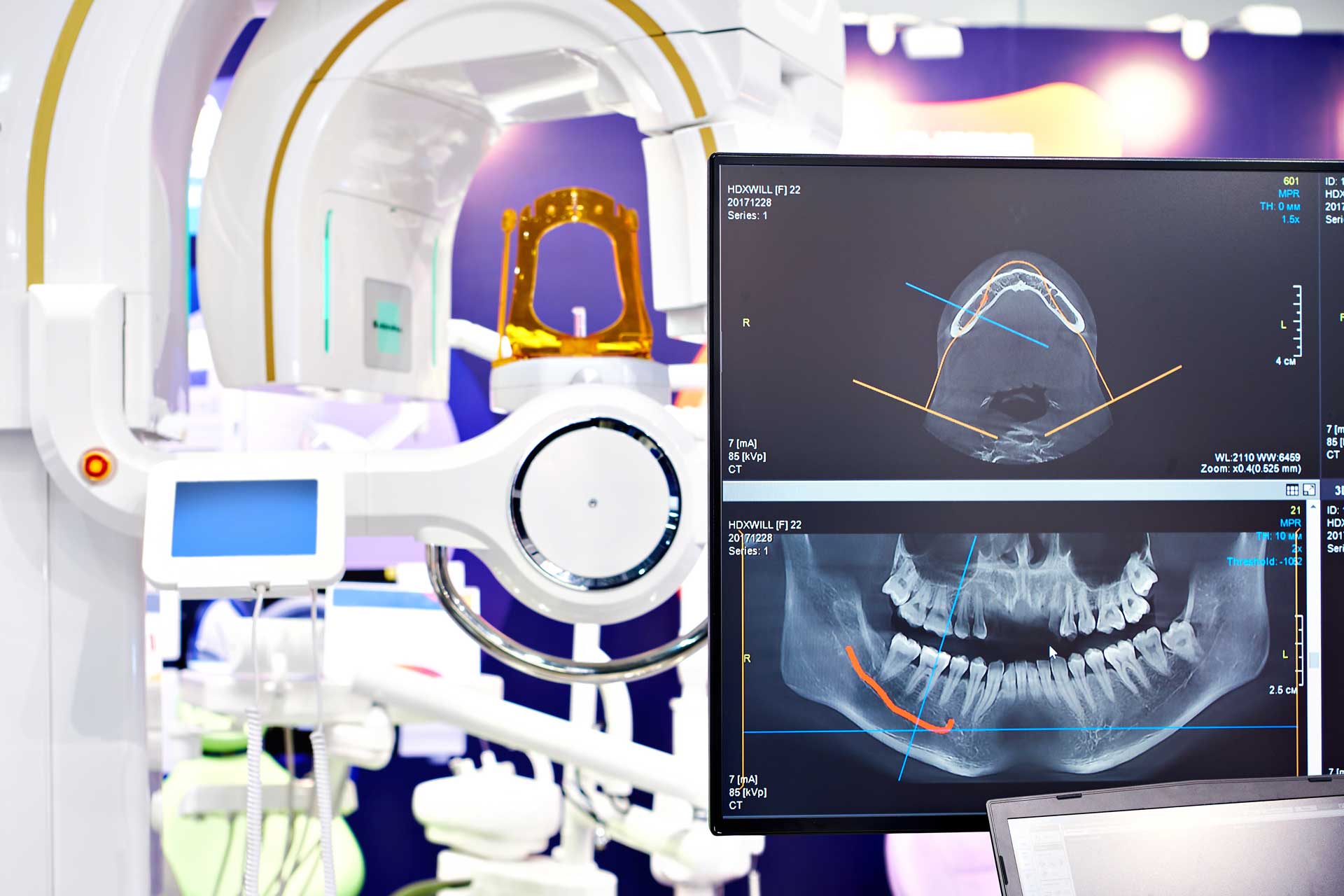
3D tomography
Computed tomography is one of the most excellent diagnostic imaging tools with a wide range of clinical applications. Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), also known as digital volumetric tomography or dental 3D tomography, is a variation of computed tomography used in dentistry. The X-ray beam is cone-shaped, and the short examination time and one rotation of the tube around the patient’s head make the radiation dose up to several hundred times lower than that of general medical CT.
CBCT application
- endodontics (including root fracture, evaluation of tooth root anatomy)
- caries of dental hard tissues
- oral surgery (impacted teeth, wisdom teeth, cysts, bone tumors)
- orthodontics
- toothaches that are difficult to diagnose
- periapical tissue diseases
- tooth and bone traumas
- inflammation of paranasal sinuses
- implant treatment planning